一、线性表
1.顺序储存结构的插入与删除
(1)获取元素
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class list{
public:
int a[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int length;
list(){length=sizeof(a)/4;}
};
//获取元素操作
int GetNum(list t, int length, int *p){
//判断线表是否长度为0
if(length==0){
return 0;
}
int m;
cout << "输入获取哪个元素" << endl;
cin>>m;
//确保正确输入获取的元素下标
while(m>length || m<0){
cout << "重新输入 " <<endl;
cin>>m;
}
length=m;
*p=t.a[length-1];
return *p;
}
int main(){
list t;
int q;
q=GetNum(t,t.length,&q);
cout << "这个数是" <<q<<endl;
}(2)插入
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXSIZE 100
class list{
private:
int data[MAXSIZE];
int length=0;
public:
void inlist(int len);
void putlist(int len);
void onlist(int len);
};
int main()
{
list T;
int len;
cout <<"请输入线性表的长度"<<endl;
cin>>len;
T.inlist(len);
T.putlist(len);
T.onlist(len);
}
inline void list::inlist(int len){
if(len<1||len>MAXSIZE){
cout <<"输入不规范"<<endl;
}else
{
cout <<"输入元素"<< endl;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cin>>data[i];
}
length=len;
}
}
inline void list::putlist(int len){
cout << "输入的元素为" << endl;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cout <<data[i]<<endl;
}
}
inline void list::onlist(int len){
int n,point;
cout <<"插入的个数"<<endl;
cin >> n;
if(len+n>=MAXSIZE && n>len+1){
cout <<"插入失败"<< endl;
}else
{
cout <<"插入成功"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout <<"插入的第"<<i+1<<"个数的位置"<<endl;
cin>>point;
cout <<"插入的数字是"<<endl;
for(int j=length-1;j>=point-1;j--){
data[j+1]=data[j];
}
cin>>data[point-1];
length++;
list::putlist(length);
}
}
}(3)删除
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXSIZE 100
class list{
private:
int data[MAXSIZE];
int length=0;
public:
void inlist(int len);
void putlist(int len);
void onlist(int len);
};
int main()
{
list T;
int len;
cout <<"请输入线性表的长度"<<endl;
cin>>len;
T.inlist(len);
T.putlist(len);
T.onlist(len);
}
inline void list::inlist(int len){
if(len<1||len>MAXSIZE){
cout <<"输入不规范"<<endl;
}else
{
cout <<"输入元素"<< endl;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cin>>data[i];
}
length=len;
}
}
inline void list::putlist(int len){
cout << "输入的元素为" << endl;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cout <<data[i]<<endl;
}
}
inline void list::onlist(int len){
int n,point;
cout <<"删除的个数"<<endl;
cin >> n;
if(n>=MAXSIZE || n<0 ){
cout <<"删除失败"<< endl;
}else
{
cout <<"删除成功"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout <<"删除的第"<<i+1<<"个数的位置"<<endl;
cin>>point;
for(int j=point;j<=length-1;j++){
data[j-1]=data[j];
}
length--;
list::putlist(length);
}
}
}
2.链式储存结构

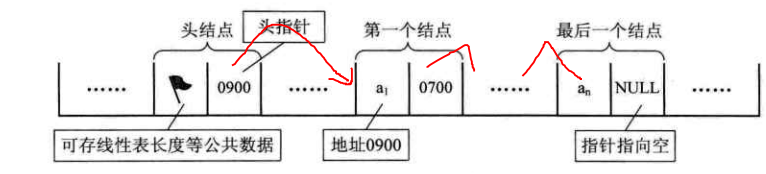
单链表
(1)初始化赋值
头插法:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node{
int date;
struct Node* next;
}Node,*PNode;//Node 相当于struct Node , *PNode 相当于struct Node*
//用PNode主要为了强调这是一个单链表,用Node*主要强调这是一个节点
PNode ListNodeInit(){
Node* L;
L=(Node* )malloc(sizeof(Node));//申请头节点空间
L->next=NULL;
int a;
cout<<"请输入节点数字"<<endl;
cin>>a;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
int t;
cin>>t;
Node* p;//创建节点
p=(Node* )malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->date=t;
p->next=L->next;
L->next=p;
int m;
}
return L;
}
void ListPrint(){
Node* O;
Node* Y=ListNodeInit();
O=Y->next;
while(O){
cout<<O->date<<" ";
O=O->next;
}
}
int main(){
ListPrint();
return 0;
}用头插法的遍历输出是逆序输出的,头插法是把每一个节点放在第一位,所以后面放在第一位的就会把之前的第一位挤到后面去
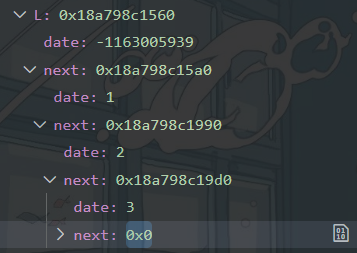
通过调试数据可以看出链表结构如下
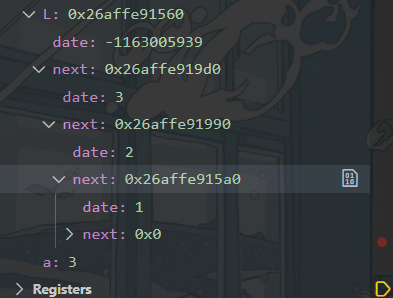
输出结果如下
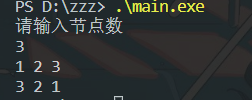
尾插法:
PNode ListNodeInit(){
Node* L;
Node* r;//定义尾指针,每次都指向最后一个节点
L=(Node* )malloc(sizeof(Node));//申请头节点空间
L->next=NULL;
r=L;//尾指针指向头节点
int a;
cout<<"请输入节点数"<<endl;
cin>>a;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
int t;
cin>>t;
Node* p;//创建节点
p=(Node* )malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->date=t;
r->next=p;//把新节点插入到r节点之后
r=p;//尾指针指向下一个节点
}
r->next=NULL;
return L;
}
尾插的聊表结构如下:
(2)查找
按位查找,返回第i个元素
// 按位查找,返回第i个数据
Node *GetData_1(PNode L, int i)
{
if (i < 0)
{
return NULL;
}
Node *p; // p指向当前指向的节点
int j = 0; // 计数,记录当前p指向的是第几个节点
p = L; // p开始指向头节点
while (p != NULL && j < i)
{
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}按值查找,返回第i个数据
Node *GetData_2(PNode L, int e)
{
Node *p; // p指向当前指向的节点
p = L->next; // 从第一个数据开始查找,头节点是没有数据域的
while(p!=NULL && p->date != e){//这里两个条件顺序不能变,不然会报错
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}查表长
int GetListLen(PNode L){
Node* s = L;
int num=0;
while(s->next!=NULL){
s = s->next;
num++;
}
return num;
}(3)插入
指定节点的后插操作
bool Set_Behind(Node* p,int i){
if(p==NULL){//这里是防止在按位插入数据操作前的GetData()传入表尾的数据的NULL
return false;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(PNode));//开辟一块空间
s->date = i;
s->next = p->next;
p->next =s;
return true;
}按位插入数据
bool Set_Wei(PNode L,int i){
Node *p = GetData_1(L, i-1);//这里要传入i-1,因为插入数据的时候是前一个数据的next指向的
int t;
cout <<"插入的数据是:";
cin>>t;
if(Set_Behind(p,t)){
return true;//如果插入成功就返回真
}else{
return false;
}
}(4)删除
指定节点p的删除
这个操作的原理就是实际上就是把p后一个节点的数据搬到p节点,实现将p节点删除
bool ListDel_1(Node* p){
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
Node* s = p->next;//让节点s指向p的下一个节点
p->date = p->next->date;//让p下一个节点的数据将p覆盖掉
p->next = s->next;//把p的指针域换成下一个节点的指针域
free(s);//释放s节点
return true;
}该代码有点bug,p->date = p->next->date,如果是删除最后一个元素,那么最后指向的NULL是没有数据域的。
按位删除节点
bool ListDel_2(PNode L,int i){
Node *p = GetData_1(L, i);//这里要传入i
if(ListDel_1(p)){
return true;//如果插入成功就返回真
}else{
return false;
}
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
int date;
struct Node *next;
} Node, *PNode; // Node 相当于struct Node , *PNode 相当于struct Node*
// 用PNode主要为了强调这是一个单链表,用Node*主要强调这是一个节点
// 尾插法创建链表
PNode ListNodeInit()
{
Node *L;
Node *r; // 定义尾指针,每次都指向最后一个节点
L = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 申请头节点空间
L->next = NULL;
r = L; // 尾指针指向头节点
int a;
cout << "请输入节点数" << endl;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
Node *p; // 创建节点
p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->date = t;
r->next = p; // 把新节点插入到r节点之后
r = p; // 尾指针指向下一个节点
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}
// 按位查找,返回第i个数据
Node *GetData_1(PNode L, int i)
{
if (i < 0)
{
return NULL;
}
Node *p; // p指向当前指向的节点
int j = 0; // 计数,记录当前p指向的是第几个节点
p = L; // p开始指向头节点
while (p != NULL && j < i)
{
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}
//按值查找,返回第i个数据
Node *GetData_2(PNode L, int e)
{
Node *p; // p指向当前指向的节点
p = L->next; // 从第一个数据开始查找,头节点是没有数据域的
while(p != NULL && p->date != e){
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
//返回表长
int GetListLen(PNode L){
Node* s = L;
int num=0;
while(s->next!=NULL){
s = s->next;
num++;
}
return num;
}
//指定节点的后插操作
bool Set_Behind(Node* p,int t){
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(PNode));//开辟一块空间
s->date = t;
s->next = p->next;
p->next =s;
return true;
}
//按位插入数据
bool Set_Wei(PNode L,int i){
Node *p = GetData_1(L, i-1);//这里要传入i-1,因为插入数据的时候是前一个数据的next指向的
int t;
cout <<"插入的数据是:";
cin>>t;
if(Set_Behind(p,t)){
return true;//如果插入成功就返回真
}else{
return false;
}
}
//指定节点的删除
bool ListDel_1(Node* p){
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
Node* s = p->next;//让节点s指向p的下一个节点
p->date = p->next->date;//让p下一个节点的数据将p覆盖掉
p->next = s->next;//把p的指针域换成下一个节点的指针域
free(s);//释放s节点
return true;
}
//按位删除数据
bool ListDel_2(PNode L,int i){
Node *p = GetData_1(L, i);//这里要传入i
if(ListDel_1(p)){
return true;//如果插入成功就返回真
}else{
return false;
}
}
// 遍历链表
void ListPrint(PNode L)
{
Node *s;
s = L->next; // 让s指向第一个元素
while (s != NULL)
{
cout << s->date << " ";
s = s->next;
}
}
int main()
{
PNode L = ListNodeInit();
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout<<"遍历这个表"<<endl;
ListPrint(L);
cout << endl;
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
int len = GetListLen(L);
cout <<"这个表长为:"<<len<<endl;
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
int i;
cout << "请输入要查找的位数:";
cin >> i;
Node *t1 = GetData_1(L, i);
cout << "第" << i << "个节点的数据是" << t1->date << endl;
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
int e;
cout << "请输入要查找的数:";
cin >> e;
Node *t2 = GetData_2(L, e);
if(t2!=NULL){
cout <<"找到了数据为"<<e<<"的元素"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"没有找到值为"<<e<<"的元素"<<endl;
}
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入要插入的位数:";
cin >> i;
bool ret = Set_Wei(L, i);
if(ret){
cout << "插入成功"<< endl;
}else{
cout << "插入失败"<< endl;
}
cout<<"插入后遍历这个表"<<endl;
ListPrint(L);
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入要删除的位数:";
cin >> i;
bool ret2 = ListDel_2(L,i);
if(ret){
cout << "删除成功"<< endl;
}else{
cout << "删除失败"<< endl;
}
cout<<"删除后遍历这个表"<<endl;
ListPrint(L);
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
return 0;
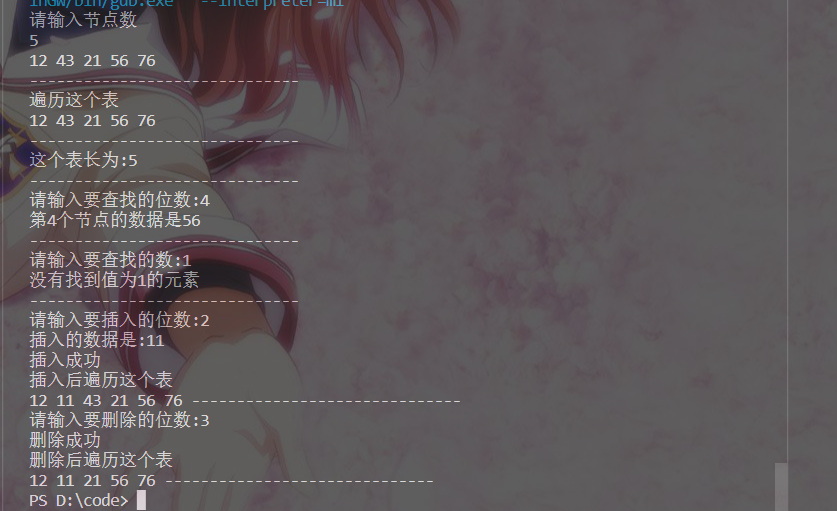
}运行结果:
双链表
双链表的核心操作与单链表基本无异,双链表多了一个前指针,指向节点的前一个节点,更方便了某些操作
(1)初始化赋值
初始化链表
bool InitDList(DPList& L){
if(L!=NULL){
L = (DNode* )malloc(sizeof(DPList));//开辟头节点
L->prior = NULL;
L->next = NULL;
}else{
return false;
}
return true;
}尾插赋值
DPList SetDList(DPList& L){
InitDList(L);//初始一个空表
int t;
DNode* r;//创建尾指针
r = L;
cout <<"请输入节点数:";
cin>>t;
cout <<"请输入数据"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
int m;
cin>>m;
DNode* p = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DPList));
p->data = m;//把数据给节点p
r->next = p;//将r的next指向p
p->prior =r;//将p的前指针指向r
r = p;//尾指针指向下一个节点
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}遍历链表
void printDList(DPList t){
DNode* s;
s = t->next;
while (s != NULL)
{
cout <<s->data<<" ";
s = s->next;
/* code */
}
}(2)插入
跟单链表操作差不多,在单链表先写了查找的函数,这里就直接写按位查找的插入操作了
bool DListInsert(DPList& L,int i,int e){
int m = DListLen(L);//计算链表长度
if(i<0 || i>m){
return false;//判断传入位置是否合适
}
DNode* p;//显示p当前指向的节点
int j = 0;//计数
p = L;//p从头节点开始,头节点是第0个数据
while(p!=NULL && j<i-1){//这里是i-1,因为后插操作使用的是前节点的next指针操作的
p = p->next;
j++;
}
//-------------------------------------以上是按位查找操作
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
DNode* s = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DPList));//开辟一个节点用于插入
s->data = e;//把数据给s节点
p->next->prior = s;//p下一个节点的前指针指向s
s->next = p->next;//将p下一个节点给s下一个节点
s->prior = p;//s的前指针指向p
p->next = s; //p的下一个节点改为s
return true;
//-------------------------------------后插操作
}上面两个操作可以跟单链表里一下分别用两个函数实现,便于代码的维护和复用
(3)删除
删除指点节点
//按位删除
bool DListDel(DPList& L,int i){
int m = DListLen(L);//计算链表长度
if(i<0 || i>m){
return false;//判断传入位置是否合适
}
DNode* p;//显示p当前指向的节点
int j = 0;//计数
p = L;//p从头节点开始,头节点是第0个数据
while(p!=NULL && j<i-1){//这里是i-1,因为后插操作使用的是前节点的next指针操作的
p = p->next;
j++;
}
//-------------------------------------以上是按位查找操作
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
DNode* s = p->next;//找到p的下一个节点
if(s == NULL){
return false;//如果下一个节点是NULL返回false
}
p->next = s->next;//把s下一个节点给p
if(s->next!=NULL){//判断s下一个节点是否是空
s->next->prior = p;//将s下一个节点的前指针指向p
}
free(s);//删除s
return true;
//-------------------------------------后插操作
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* prior;//前节点
struct Node* next;//后节点
/* data */
}DNode,*DPList;
//初始化双链表
bool InitDList(DPList& L){
if(L!=NULL){
L = (DNode* )malloc(sizeof(DPList));//开辟头节点
L->prior = NULL;
L->next = NULL;
}else{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//建立双链表
DPList SetDList(DPList& L){
InitDList(L);//初始一个空表
int t;
DNode* r;//创建尾指针
r = L;
cout <<"请输入节点数:";
cin>>t;
cout <<"请输入数据"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
int m;
cin>>m;
DNode* p = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DPList));
p->data = m;//把数据给节点p
r->next = p;//将r的next指向p
p->prior =r;//将p的前指针指向r
r = p;//尾指针指向下一个节点
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}
//遍历链表
void printDList(DPList t){
DNode* s;
s = t->next;
while (s != NULL)
{
cout <<s->data<<" ";
s = s->next;
/* code */
}
}
//计算链表长度
int DListLen(DPList L){
int num = 0;
if(L==NULL){
return num;
}else{
DNode* s;
s = L;
while (s->next!=NULL)
{
s = s->next;
num++;
}
}
return num;
}
//按位插入
bool DListInsert(DPList& L,int i,int e){
int m = DListLen(L);//计算链表长度
if(i<0 || i>m){
return false;//判断传入位置是否合适
}
DNode* p;//显示p当前指向的节点
int j = 0;//计数
p = L;//p从头节点开始,头节点是第0个数据
while(p!=NULL && j<i-1){//这里是i-1,因为后插操作使用的是前节点的next指针操作的
p = p->next;
j++;
}
//-------------------------------------以上是按位查找操作
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
DNode* s = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DPList));//开辟一个节点用于插入
s->data = e;//把数据给s节点
p->next->prior = s;//p下一个节点的前指针指向s
s->next = p->next;//将p下一个节点给s下一个节点
s->prior = p;//s的前指针指向p
p->next = s; //p的下一个节点改为s
return true;
//-------------------------------------后插操作
}
//按位删除
bool DListDel(DPList& L,int i){
int m = DListLen(L);//计算链表长度
if(i<0 || i>m){
return false;//判断传入位置是否合适
}
DNode* p;//显示p当前指向的节点
int j = 0;//计数
p = L;//p从头节点开始,头节点是第0个数据
while(p!=NULL && j<i-1){//这里是i-1,因为后插操作使用的是前节点的next指针操作的
p = p->next;
j++;
}
//-------------------------------------以上是按位查找操作
if(p==NULL){
return false;
}
DNode* s = p->next;//找到p的下一个节点
if(s == NULL){
return false;//如果下一个节点是NULL返回false
}
p->next = s->next;//把s下一个节点给p
if(s->next!=NULL){//判断s下一个节点是否是空
s->next->prior = p;//将s下一个节点的前指针指向p
}
free(s);//删除s
return true;
//-------------------------------------后插操作
}
int main(){
DPList L;
L = SetDList(L);
cout<<"----------------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"插入前"<<endl;
printDList(L);
cout <<endl;
cout<<"----------------------------"<<endl;
cout <<"请分别输入插入的位置和数据:";
int i;
int e;
cin>>i;
cin>>e;
DListInsert(L,i,e);
cout<<"插入后"<<endl;
printDList(L);
cout <<endl;
cout<<"----------------------------"<<endl;
cout <<"请输入删除的位置:";
cin>>i;
DListDel(L,i);
cout<<"删除后"<<endl;
printDList(L);
cout <<endl;
cout<<"----------------------------"<<endl;
return 0;
}循环链表
循环链表有循环单链表和循环双链表,本质都是一样的,不过循环链表中最后一个节点的指向不在是NULL而是头节点,这也就意味着在循环链表操作中不存在NULL的判断
静态链表
静态链表实质上就是由数组实现的链表
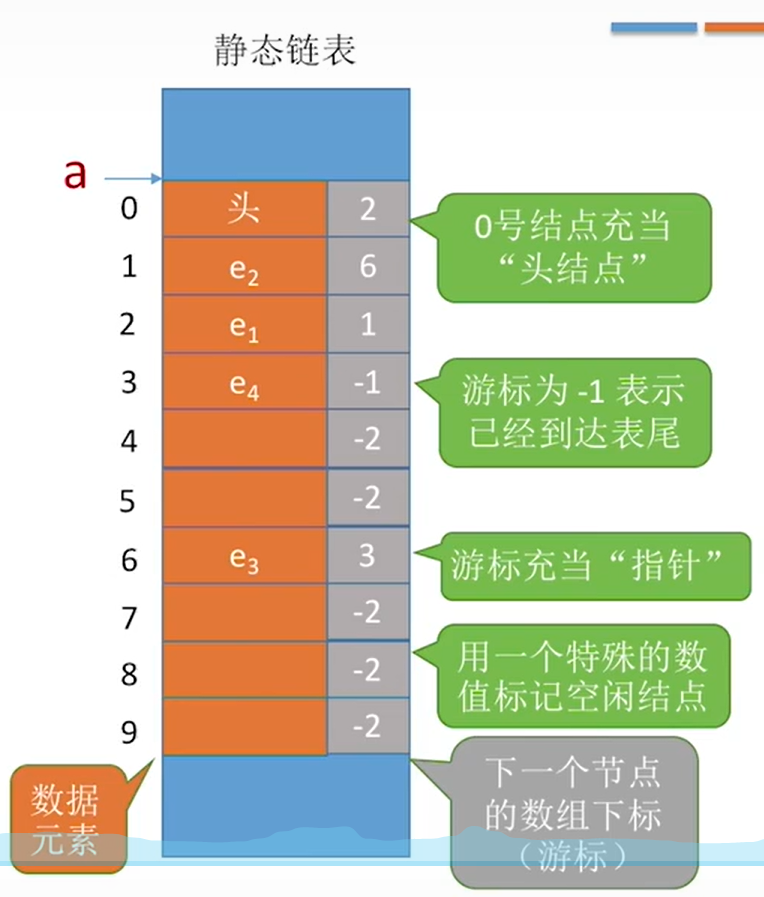
数据被存放在一块连续的空间内,定义方式
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct{
int data;
int next;
}SList[MaxSize];这里的next保存的是下一个数据所在的位置

二、栈与队列
1.栈
(1)栈的顺序储存
功能实现
定义顺序栈
typedef struct{
int data[MaxSize];//静态数组存放元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SStack;初始化栈
SStack InitSStack(){
SStack SS;
SS.top=-1;//栈顶指针指向-1
return SS;
}判断栈是否为空
bool If_empty(SStack SS){
return SS.top==-1;
}判断是否满
bool If_full(SStack SS){
return SS.top==MaxSize-1;
}进栈
bool Push(SStack& SS,int x){
if(SS.top==MaxSize-1){
cout <<"入栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
SS.data[++SS.top] = x;
return true;
}出栈
int pop(SStack& SS){
if(If_empty(SS)){
cout<<"出栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
int item;
item = SS.data[SS.top];
SS.top--;
return item;
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 10
//定义顺序栈
typedef struct{
int data[MaxSize];//静态数组存放元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SStack;
//初始化栈
SStack InitSStack(){
SStack SS;
SS.top=-1;//栈顶指针指向-1
return SS;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool If_empty(SStack SS){
return SS.top==-1;
}
//判断栈是否已满
bool If_full(SStack SS){
return SS.top==MaxSize-1;
}
//进栈
bool Push(SStack& SS,int x){
if(SS.top==MaxSize-1){
cout <<"入栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
SS.data[++SS.top] = x;
return true;
}
//出栈并返回值
int pop(SStack& SS){
if(If_empty(SS)){
cout<<"出栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
int item;
item = SS.data[SS.top];
SS.top--;
return item;
}
int main(){
SStack SS=InitSStack();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
Push(SS,i);
}
int item;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
item=pop(SS);
cout <<item<<" ";
}
return 0;
}(2)栈的链式储存
功能实现
定义链式节点
typedef struct ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode* next;
}ListNode;定义链式栈类
class ListStack{
private:
ListNode* top;
int size;//队列长度
public:
ListStack();//构造函数初始化队列
void push(int x);//入队操作
bool If_empty();//判断队列是否为空
bool pop();//出队操作
int GetTop();//获取栈顶元素
void print(ListStack L);//通过出队和获取栈顶元素实现遍历
};函数实现
ListStack::ListStack(){
top = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
//为top开辟空间,不开辟会报错
top->next = NULL;//不带头节点
size = 0;
}
void ListStack::push(int x){
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//开辟一个节点
p->data =x;
p->next = top->next;
top->next = p;
size++;
}
bool ListStack::If_empty(){
return top->next==NULL;
}
bool ListStack::pop(){
if(ListStack::If_empty()){
return false;//队空返回false
}
ListNode* s = top->next;
top->next = s->next;
free(s);
size--;
return true;
}
int ListStack::GetTop(){
return top->next->data;
}
void ListStack::print(ListStack L){
int t = L.size;
int item;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
item = L.GetTop();
cout <<item<<" ";
L.pop();
}
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义链式节点
typedef struct ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode* next;
}ListNode;
//定义链式队列类
class ListStack{
private:
ListNode* top;
int size;//队列长度
public:
ListStack();//构造函数初始化队列
void push(int x);//入队操作
bool If_empty();//判断队列是否为空
bool pop();//出队操作
int GetTop();//获取栈顶元素
void print(ListStack L);//通过出队和获取栈顶元素实现遍历
};
ListStack::ListStack(){
top = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
//为top开辟空间,不开辟会报错
top->next = NULL;//不带头节点
size = 0;
}
void ListStack::push(int x){
ListNode* p = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//开辟一个节点
p->data =x;
p->next = top->next;
top->next = p;
size++;
}
bool ListStack::If_empty(){
return top->next==NULL;
}
bool ListStack::pop(){
if(ListStack::If_empty()){
return false;//队空返回false
}
ListNode* s = top->next;
top->next = s->next;
free(s);
size--;
return true;
}
int ListStack::GetTop(){
return top->next->data;
}
void ListStack::print(ListStack L){
int t = L.size;
int item;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
item = L.GetTop();
cout <<item<<" ";
L.pop();
}
}
int main(){
ListStack L;
L.push(1);
L.push(2);
L.push(3);
L.push(4);
L.push(5);
L.print(L);
return 0;
}(3)栈在括号匹配中的应用
在程序中的括号匹配可以利用栈来实现
算法实现
bool BraceMatch(char* str,int len){
SStack SS = InitSStack();//初始化栈
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(str[i]=='(' || str[i]=='[' || str[i]=='{'){
Push(SS,str[i]);//扫描到左括号入栈
}else{
if(If_empty(SS))
return false;//如果没有扫描到左括号并且栈为空返回false
//这个时候左括号扫描完了,可以出栈左括号了
char item = pop(SS);//用item接受出栈的值进行匹配
if(str[i]==')' && item!='('){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
if(str[i]==']' && item!='['){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
if(str[i]=='}' && item!='{'){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
}
}
return If_empty(SS);//如果全部成功出栈返回true
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 10
//定义顺序栈
typedef struct{
char data[MaxSize];//静态数组存放元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SStack;
//初始化栈
SStack InitSStack(){
SStack SS;
SS.top=-1;//栈顶指针指向-1
return SS;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool If_empty(SStack SS){
return SS.top==-1;
}
//判断栈是否已满
bool If_full(SStack SS){
return SS.top==MaxSize-1;
}
//进栈
bool Push(SStack& SS,char x){
if(SS.top==MaxSize-1){
cout <<"入栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
SS.data[++SS.top] = x;
return true;
}
//出栈并返回值
char pop(SStack& SS){
if(If_empty(SS)){
cout<<"出栈失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
char item;
item = SS.data[SS.top];
SS.top--;
return item;
}
bool BraceMatch(char* str,int len){
SStack SS = InitSStack();//初始化栈
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(str[i]=='(' || str[i]=='[' || str[i]=='{'){
Push(SS,str[i]);//扫描到左括号入栈
}else{
if(If_empty(SS))
return false;//如果没有扫描到左括号并且栈为空返回false
//这个时候左括号扫描完了,可以出栈左括号了
char item = pop(SS);//用item接受出栈的值进行匹配
if(str[i]==')' && item!='('){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
if(str[i]==']' && item!='['){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
if(str[i]=='}' && item!='{'){
return false;//括号不匹配
}
}
}
return If_empty(SS);//如果全部成功出栈返回true
}
int main(){
char* str;
int len = 6;
for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){
cin>>str[i];
}
if(BraceMatch(str,len)){
cout <<"匹配成功";
}else{
cout <<"匹配失败";
}
return 0;
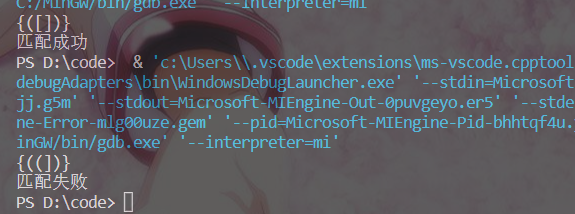
}
(4)栈在表达式求值中的应用
计算中缀表达式
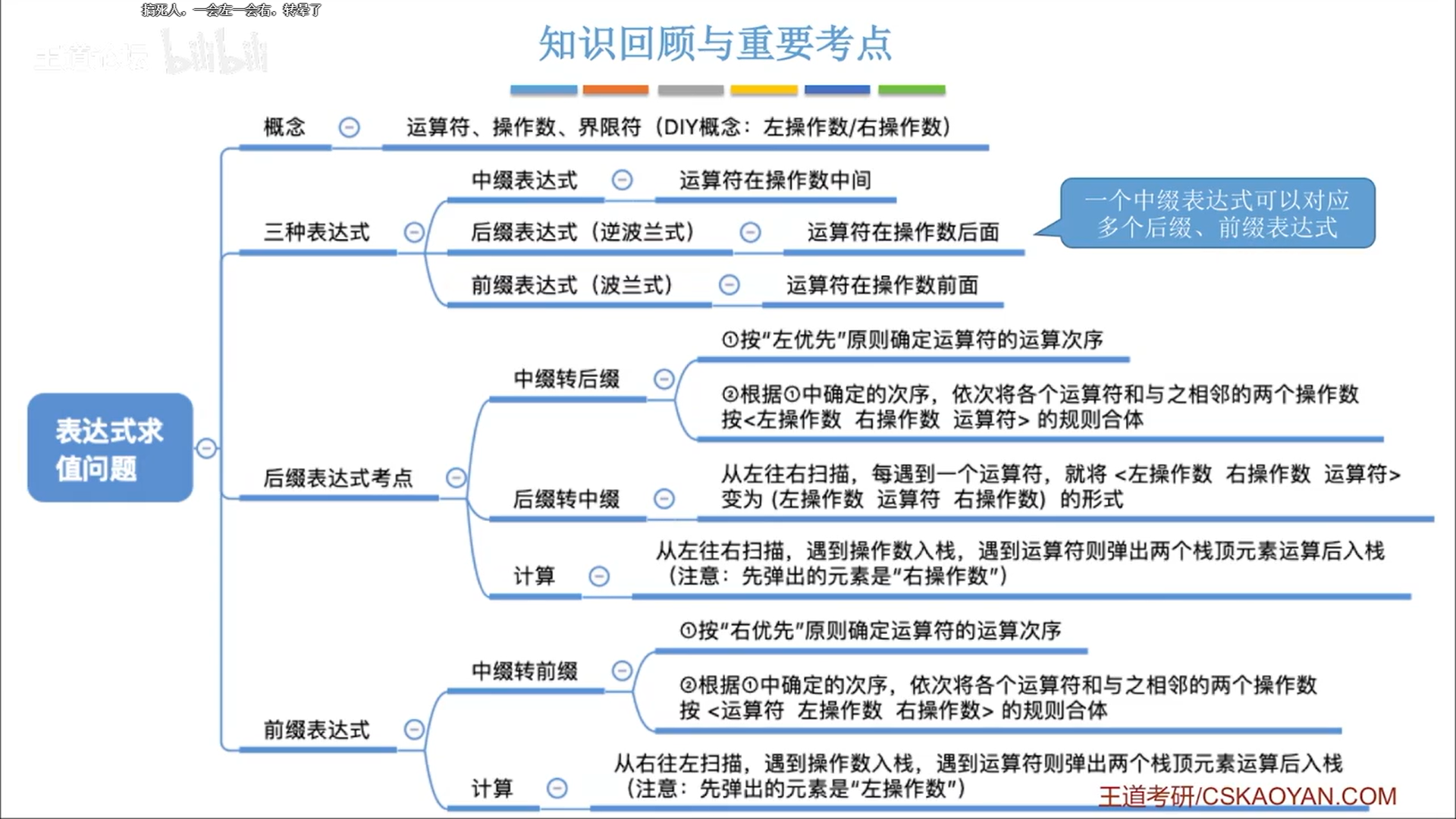

功能实现
void ListStack::compute(ListStack L1,ListStack L2){
char a;//运算符栈传入的是运算的ascll码对应的,用char接收自动转化
T b,c,d;
a = L1.pop();
b = L2.pop();
c = L2.pop();
if(a=='*'){
d = c*b;//这里的c b位置不能改变,因为出栈的顺序是固定的
}else if(a=='/'){
d = c/b;
}else if(a=='+'){
d = c+b;
}else if(a=='-'){
d = c-d;
}else{
//cout <<"erro"<<endl;
}
L2.push(d);//将运算后的值重新压入栈中
}
//计算中缀表达式
//思路初始化两个栈,一个用来放操作数,一个用来放运算符
//要是遇到了操作数压入操作数栈
//要是遇到运算符压入运算符栈(弹出运算的时候也会弹出两个操作数进行计算,并将结果放回操作数栈)用compute函数实现
double ListStack::Cal(char str[100]){
int len = 0;
for(int i = 0;str[i]!='\0';i++){
len++;//计算表达式长度
}
ListStack L1;
ListStack L2;
//(1+2)*3-(2+2)/4
for(int i =0;i<=len;i++){
if('0'<=str[i] && str[i]<='9'){//判断是不是数字
L2.push(str[i]-48);//因为char传入时转成ascll,减去48就是原来的值
continue;//存入一个后直接开始下一轮循环
}//这是当表达式的开头不是括号的时候
if(str[i]=='(' || L1.If_empty()){//如果开头是括号就将(压入栈,如果不是,那么执行了上面的if,下一个也肯定是运算符
L1.push(str[i]);//这里不是存数字直接存就可以了
continue;
}
if(str[i]==')'){//如果是)则要开始计算括号里的,)是不需要入栈的,只是一个判断的作用
char item = L1.GetTop();
//这个地方我开始写的时候是while(item!='('),这样就写成一个死循环了,因为现在的item就是开始的值静态的,这样写循环里要加一句item = L1.GetTop();重新获取写的栈顶值
while(item!='('){//如果栈里不是两个连续的( (,这里用while不用if是因为可能括号里不止一个运算符 列入((1+2*2/2)*3)-(2+2)/4
this->compute(L1,L2);//计算
item = L1.GetTop();
}
L1.pop();//将栈中的(出栈
continue;
}
if(str[i]=='*'||str[i]=='/'){
T item2 = L1.GetTop();//看上一个运算符是否已经是*或/,如果是则先运算上一个* / 例如((1+2*2/2)*3)-(2+2)/4
if(item2 == '/' || item2 == '*'){
this->compute(L1,L2);
}
L1.push(str[i]);//在把这个运算符压入栈
continue;
}
if(str[i]=='+' || str[i]=='-'){
T item3 = L1.GetTop();
if(item3 !='('){//如果栈最上面不是(则直接运算 列如 (1+(2-3)+4)/4
this->compute(L1,L2);
}
L1.push(str[i]);//如果是则直接进栈
continue;
}
while(!L1.If_empty()){//如果开头不是(,运算到最后栈不为空则继续运算
this->compute(L1,L2); //例如1+2-(1*2)
}
}
T num;
num = L2.GetTop();//获取运算值
return num;
}测试代码
void test(){
ListStack L;
char str[100];
cout <<"请输入计算的中缀式:";
cin>>str;
int num = L.Cal(str);
cout <<num;
}2.队列
(1)队列的顺序储存
功能实现
队列的定义
typedef struct{
int data[MaxSize];//用静态数组存放队列,一块连续的的储存空间
int front,rear;//队头指针和队尾指针,队尾指针是指向下一个要插入元素的位置,而不是最后一个元素
int size;//记录队列长度
}SQueue;初始化一个队列
SQueue InitSQueue(){
SQueue SQ;
SQ.front=SQ.rear=0;//开始的时候队头和队尾指针都指向,起始位置
SQ.size=0;
return SQ;
}判断队列是否为空
bool If_empty(SQueue SQ){
if(SQ.front==SQ.rear&&SQ.size==0){//当两个指针指向同一块位置时判断为空且长度为0
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}判断队列是否已满
//判断队列是否已满
bool If_full(SQueue SQ){
if(SQ.size==MaxSize){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}入队操作
bool In_queue(SQueue& SQ,int e){
bool ret = If_full(SQ);
if(ret){
cout<<"这个队列已满,入队失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
SQ.data[SQ.rear]=e;//将数据入队
SQ.rear=(SQ.rear+1)%MaxSize;//实现循环队列
SQ.size++;//队列长度加1
return true;
}SQ.rear=(SQ.rear+1)%MaxSize;这一句要模上Maxsize之后当rear达到10的时候就会回到0,实现循环队列
出队操作
int Out_queue(SQueue& SQ,int& x){
if(If_empty(SQ)){
cout <<"出队失败"<<endl;//判读队列是否为空
return 0;
}
x=SQ.data[SQ.front];
SQ.front=(SQ.front+1)%MaxSize;
SQ.size--;
return x;
}因为队列不能够遍历,所以用出队的返回值可以模拟遍历
完整代码
//顺序存储实现的队列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxSize 10
//队列的定义
typedef struct{
int data[MaxSize];//用静态数组存放队列,一块连续的的储存空间
int front,rear;//队头指针和队尾指针,队尾指针是指向下一个要插入元素的位置,而不是最后一个元素
int size;//记录队列长度
}SQueue;
//初始化一个顺序队列
SQueue InitSQueue(){
SQueue SQ;
SQ.front=SQ.rear=0;//开始的时候队头和队尾指针都指向,起始位置
SQ.size=0;
return SQ;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool If_empty(SQueue SQ){
if(SQ.front==SQ.rear&&SQ.size==0){//当两个指针指向同一块位置时判断为空
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//判断队列是否已满
bool If_full(SQueue SQ){
if(SQ.size==MaxSize){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//入队操作
bool In_queue(SQueue& SQ,int e){
bool ret = If_full(SQ);
if(ret){
cout<<"这个队列已满,入队失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
SQ.data[SQ.rear]=e;//将数据入队
SQ.rear=(SQ.rear+1)%MaxSize;//实现循环队列
SQ.size++;//队列长度加1
return true;
}
//出队操作,并返回出队的值
int Out_queue(SQueue& SQ,int& x){
if(If_empty(SQ)){
cout <<"出队失败"<<endl;//判读队列是否为空
return 0;
}
x=SQ.data[SQ.front];
SQ.front=(SQ.front+1)%MaxSize;
SQ.size--;
return x;
}
int main(){
int m;
SQueue SQ = InitSQueue();
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){
In_queue(SQ,i);
}
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){
Out_queue(SQ,m);
cout <<m<<" ";
}
return 0;
}(2)队列的链式储存
功能实现
队列定义
typedef struct ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode* next;
}ListNode;队列类建立
class ListQueue{
private:
ListNode* front;//队头指针
ListNode* rear;//队尾指针
int size;//队列长度
public:
ListQueue();//构造函数初始化队列
~ListQueue();//析构函数销毁队列
void In_Queue(int x);//入队操作
bool If_empty();//判断队列是否为空
bool Out_Queue(int& x);//出队操作
};函数实现
ListQueue::ListQueue(){
front = rear =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//队头和队尾指针都指向头节点
front->next=NULL;
size=0;
}
void ListQueue::In_Queue(int x){
ListNode* s = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
s->data = x;
s->next =NULL;
rear->next =s;//让rear的next指针域指向s
rear = s;//将s改为尾指针
size++;
}
bool ListQueue::If_empty(){
if(this->front==this->rear){
cout <<"这个队列是空的"<<endl;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool ListQueue::Out_Queue(int& x){
if(this->If_empty()){
cout <<"出队失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
ListNode* p = front->next;//用p指向这次要出队的节点
x = p->data;//用x接收要出队节点的数据
front->next = p->next;//修改头节点指向
if(rear == p){//如果要删除的是最后一个节点
front = rear;
}
free(p);//删除节点
size--;
return true;
}
ListQueue::~ListQueue(){
if(front!=rear){
ListNode* p = front->next;//用p指向这次要出队的节点
front->next = p->next;//修改头节点指向
if(rear == p){//如果要删除的是最后一个节点
front = rear;
}
free(p);
}
}完整代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//定义链式节点
typedef struct ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode* next;
}ListNode;
//定义链式队列类
class ListQueue{
private:
ListNode* front;//队头指针
ListNode* rear;//队尾指针
int size;//队列长度
public:
ListQueue();//构造函数初始化队列
~ListQueue();//析构函数销毁队列
void In_Queue(int x);//入队操作
bool If_empty();//判断队列是否为空
bool Out_Queue(int& x);//出队操作
};
ListQueue::ListQueue(){
front = rear =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//队头和队尾指针都指向头节点
front->next=NULL;
size=0;
}
void ListQueue::In_Queue(int x){
ListNode* s = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
s->data = x;
s->next =NULL;
rear->next =s;//让rear的next指针域指向s
rear = s;//将s改为尾指针
size++;
}
bool ListQueue::If_empty(){
if(this->front==this->rear){
cout <<"这个队列是空的"<<endl;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool ListQueue::Out_Queue(int& x){
if(this->If_empty()){
cout <<"出队失败"<<endl;
return false;
}
ListNode* p = front->next;//用p指向这次要出队的节点
x = p->data;//用x接收要出队节点的数据
front->next = p->next;//修改头节点指向
if(rear == p){//如果要删除的是最后一个节点
front = rear;
}
free(p);//删除节点
size--;
return true;
}
ListQueue::~ListQueue(){
if(front!=rear){
ListNode* p = front->next;//用p指向这次要出队的节点
front->next = p->next;//修改头节点指向
if(rear == p){//如果要删除的是最后一个节点
front = rear;
}
free(p);
}
}
int main(){
ListQueue L;
for(int i =0;i<10;i++){
L.In_Queue(i);
}
int m;
for(int i =0;i<5;i++){
L.Out_Queue(m);
cout <<m<<" ";
}
}三、串
串,即字符串(String),是由零个或多个字符组成的有限序列。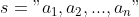
其中,s是串名,引号(单/双引号都可)括起来的字符序列是串的值;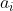 可以是字母、数字或其他字符;字符下标从1开始,串中字符的个数n称为串的长度。n=0时的串称为空串(用∅表示)。
可以是字母、数字或其他字符;字符下标从1开始,串中字符的个数n称为串的长度。n=0时的串称为空串(用∅表示)。
基本操作实现就不做了,这里主要是两种匹配算法
朴素匹配算法
//朴素匹配算法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int test(){
char a[10],b[10];
cin>>a;
cin>>b;
int i =0;int j=0;
while(a[i]!='\0' && b[j]!='\0'){
if(a[i]==b[j]){
i++;
j++;
}else{
i=i-j+1;
j=0;
}
}
if(b[j]=='\0'){//如果子串指向了\0,返回匹配的位置
return i-j;
}else{//如果没有找到,指向的是主串的\0运行else
return -1;
}
}
int main(){
int m=test();
if(m==-1){
cout <<"匹配失败";
}else{
cout <<"匹配的位置是:"<<m;
}
return 0;
}算是暴力求解
KMP算法
四、树
主要讨论二叉树
顺序储存
//顺序存储结构
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define Max 100
#define ElemType int
typedef ElemType BiTree[Max];//定义二叉树
class Mytree{
private:
BiTree tree;
int size = 0;
public:
Mytree(){}
void InitBiTree();//初始化一个树
void printBiTree();//遍历树(层次遍历)
ElemType FindParent(ElemType e);//查找父节点
ElemType LeftChild(ElemType e);//查找左孩子
ElemType RightChild(ElemType e);//查找有孩子
ElemType Gettree(ElemType e);//获取节点值
bool EmptyTree();//判断是否是空树
};
void Mytree::InitBiTree(){
ElemType node;
cout<<"请按层次从左向右输入节点,空节点用0表示,按1010停止输入"<<endl;
int i = 1;
while(cin>>node){
if(node == 1010){
break;
}
tree[i] = node;
i++;
size++;
}
}
void Mytree::printBiTree(){
//层次遍历
for(int i =1;i<=size;i++){
cout<<tree[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
ElemType Mytree::FindParent(ElemType e){
if(EmptyTree()) cout<<"这是个空树"<<endl;
if(e == 1) cout<<"根节点没有父节点"<<endl;
if(tree[e] == 0) { cout<<"不存在这个节点"; return -1;}
for(int i =2;i<=size;i++){
if(i == e){
return tree[i/2];
}
}
return -1;
}
ElemType Mytree::LeftChild(ElemType e){
if(EmptyTree()) cout<<"这是个空树"<<endl;
if(tree[e] == 0) { cout<<"不存在这个节点"; return -1;}
for(int i =2;i<=size;i++){
if(i == e){
if(i*2<size && tree[i*2]!=0){
return tree[i*2];
}else{
cout<<"当前节点没有左孩子"<<endl;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
ElemType Mytree::RightChild(ElemType e){
if(EmptyTree()) cout<<"这是个空树"<<endl;
if(tree[e] == 0) { cout<<"不存在这个节点"; return -1;}
for(int i =2;i<=size;i++){
if(i == e){
if(i*2+1<size && tree[i*2+1]!=0){
return tree[i*2+1];
}else{
cout<<"当前节点没有右孩子"<<endl;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
bool Mytree::EmptyTree(){
if(size == 0){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
ElemType Mytree::Gettree(ElemType e){
return tree[e];
}
int main(){
Mytree a;
int tmp;
a.InitBiTree();
a.printBiTree();
cout<<"-----------------"<<endl;
cout<<"请输入想要查询的节点"<<endl;
cin>>tmp;
cout<<"这个节点的的值是:"<<a.Gettree(tmp)<<endl;
cout<<"这个节点的父节点:"<<a.FindParent(tmp)<<endl;
cout<<"这个节点的左孩子:"<<a.LeftChild(tmp)<<endl;
cout<<"这个节点的右孩子:"<<a.RightChild(tmp)<<endl;
return 0;
}这种方式适合存储完全二叉树,不然的话会浪费大量空间
链式存储
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ElemType int
typedef struct BiTreeNode//定义结构体
{
ElemType data; //数据域
BiTreeNode *lChild;//左孩子
BiTreeNode *rChlid;//右孩子
} BiTreeNode, *BiTree;
//先序创建二叉树
void CreateBiTree(BiTree &T){
ElemType ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == -1)
T = NULL;
else
{
T = new BiTreeNode;
T->data = ch;
CreateBiTree(T->lChild);
CreateBiTree(T->rChlid);
}
}
//中序遍历
void GetMid(BiTree T){
if(T){
GetMid(T->lChild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
GetMid(T->rChlid);
}
}
//先序遍历
void GetFrist(BiTree T){
if(T){
cout<<T->data<<" ";
GetMid(T->lChild);
GetMid(T->rChlid);
}
}
//后序遍历
void GetLast(BiTree T){
if(T){
GetMid(T->lChild);
GetMid(T->rChlid);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
}
}
int main(void)
{
BiTree T;
cout<<"请输入先序遍历顺序下各个结点的值,-1表示没有结点:"<<endl;
CreateBiTree(T);
GetMid(T);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"---------------"<<endl;
GetFrist(T);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"---------------"<<endl;
GetLast(T);
return 0;
}二叉树的链式存储递归用的比较多
哈夫曼树
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
typedef struct HuFuNode
{
int weight;
int parent, LTree, RTree;
}HuFuNode, *PHuFuNode;
void Select(PHuFuNode HuFuNode, int n, int &s1, int &s2)
{
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(HuFuNode[i].parent == 0){
s1 = i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(HuFuNode[i].parent == 0 && HuFuNode[s1].weight > HuFuNode[i].weight)
s1 = i;
}
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++){
if(HuFuNode[j].parent == 0 && j != s1){
s2 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++){
if(HuFuNode[j].parent == 0 && HuFuNode[s2].weight > HuFuNode[j].weight && j != s1)
s2 = j;
}
}
void initHuFuNode(PHuFuNode &H, int n)
{
if(n <= 1) return;
int m = 2*n - 1; //数组共2n - 1个元素
H = new HuFuNode[m + 1]; //0号单元未用,H[m]表示根节点
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
H[i].parent = 0;
H[i].LTree = 0;
H[i].RTree = 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> H[i].weight;
cout << endl;
for(int i = n + 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int s1, s2;
Select(H, i, s1, s2);
H[s1].parent = i;
H[s2].parent = i;
H[i].LTree = s1;
H[i].RTree = s2;
H[i].weight = H[s1].weight + H[s2].weight;
}
for(int i =1 ;i<=m;i++){
cout<<H[i].weight<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
PHuFuNode HuFuNode;
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
initHuFuNode(HuFuNode, n);
return 0;
}哈夫曼编码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define Elemtype int
#define max 100
using namespace std;
//哈曼树定义
typedef struct HuffCode{
Elemtype weight;//权重
int lchild;
int rchild;
int parent;//定义左右孩子,双亲节点
}codeNode,Huffmancode[max];
typedef char** cd;
//第一个参数是传入数组,第二个值是数组遍历的终点值,用s1,s2返回两个最小值
void select(Huffmancode HC,int n,int& s1,int& s2){
for(int i = 1;i<n;i++){
if(HC[i].parent==0){
s1 = i;
break;
}
}
for(int i = 1;i<n;i++){
if(HC[i].parent==0 && HC[s1].weight>HC[i].weight){
s1 = i;
}
}
for(int j = 1;j<n;j++){
if(HC[j].parent==0 && j!=s1){
s2 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j = 1;j<n;j++){
if(HC[j].parent==0 && HC[s2].weight>HC[j].weight && j!=s1){
s2 = j;
}
}
}
//哈夫曼树的构建
void Creat_Huff(Huffmancode& HC,int n){//n为节点数量
int m = 2*n-1;//需要m大小的数组存数据
int i,s1,s2;//s1,s2用来返回最小的两个值
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){//初始化
HC[i].parent = 0;
HC[i].lchild = 0;
HC[i].rchild = 0;
cin>>HC[i].weight;
}
//处理后面的节点
for(i=n+1;i<=m;i++){
HC[i].parent = 0;
HC[i].lchild = 0;
HC[i].rchild = 0;
HC[i].weight = 0;
}
//选出数组中最小的两个树,构建哈夫曼树
for(i=n+1;i<=m;i++){
select(HC,i,s1,s2);
HC[i].weight = HC[s1].weight+HC[s2].weight;
HC[i].lchild = s1;
HC[i].rchild = s2;
HC[s1].parent = i;
HC[s2].parent = i;
}
cout<<"n"<<" "<<"w"<<" "<<"p"<<" "<<"l"<<" "<<"r"<<endl;
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++){
cout<<i<<" "<<HC[i].weight<<" "<<HC[i].parent<<" "<<HC[i].lchild<<" "<<HC[i].rchild<<endl;
cout<<left;
}
}
//----------------------------------------------------以上是哈夫曼树的实现在上一节已经实现
//哈夫曼编码实现
void Creat_code(Huffmancode& HC,cd& code,int n){
code = new char*[n+1]; //分配n个字符编码的头指针矢量
char* a = new char[n];//分配临时变量用来存编码
a[n-1] = '\0';//编码结束符
for(int i =1;i<=n;i++){//逐个字符求哈夫曼编码
int start = n-1;//开始存放的位置,因为n-1位放的是\0,起始设置在\0
int c = i;//要找的节点c
int f = HC[i].parent;//设置双亲节点的初始值
while(f!=0){//从叶子节点开始回溯,寻找双亲节点为0的位置,也就是根节点
--start;//初始strar指向\0
if(HC[f].lchild == c){
a[start]='0';//双亲节点的左孩子为c则设置为0
}else{
a[start]='1';
}
c = f;//将这个双亲节点变为孩子节点
f = HC[f].parent;//下一个要找的双亲节点位置
}
code[i] = new char [n-start];
strcpy(code[i],&a[start]);
}
delete a;
}
int main(){
Huffmancode HC;//创建哈夫曼树
int n;
cin>>n;
cd code;
Creat_Huff(HC,n);
Creat_code(HC,code, n);
for(int i =1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<code[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}五、图
邻接矩阵存储
实现步骤
- 输入节点数,和边数
- 输入节点信息,存入一个数组中
- 初始化邻接矩阵,如果是图初始化为0,如果是网,初始化无穷大
- 依次输入每条边依附的两个节点,如果有权值,还要输入权值
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
/* 1. 输入节点数,和边数
2. 输入节点信息,存入一个数组中
3. 初始化邻接矩阵,如果是图初始化为0,如果是网,初始化无穷大
4. 依次输入每条边依附的两个节点,如果有权值,还要输入权值 */
//两个数组一个用来存顶点表,一个用来存邻接矩阵
using namespace std;
#define min 0 //初始化值
#define MAXNum 100
typedef char vre;//顶点的数据类型
typedef int arc;//边的权值
typedef struct{
vre v[MAXNum];//创建顶点表
arc a[MAXNum][MAXNum];//创建邻接矩阵
int spot,side;//顶点数和边数
}AMGraph;
int LocateVex(AMGraph G,int v1){
for(int i =0;i<G.spot;i++){
if(G.v[i] == v1){
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
//创建无向网
void Creat_UDN(AMGraph& G){
char v1,v2;
int w;
cout<<"分别输入节点和边的数量"<<endl;
cin>>G.spot>>G.side;//输入边和点
cout<<"输入节点信息"<<endl;
for(int i =0;i<G.spot;i++){
cin>>G.v[i];//输入点的信息
}
for(int i =0;i<G.spot;i++){
for(int j =0;j<G.spot;j++){
G.a[i][j] = min;//设置边的权值
}
}//初始化边
cout<<"输入每条边依附的节点以及权值"<<endl;
for(int k =0;k<G.side;k++){
cin>>v1>>v2>>w;
int i = LocateVex(G,v1);
int j = LocateVex(G,v2);
G.a[i][j] = w;
//cout<<G.a[i][j]<<" ";
G.a[j][i] = G.a[i][j] ;
//cout<<G.a[j][i]<<endl;
}
cout<<"图的邻接矩阵为:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.spot; i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<G.spot;j++){
cout<<G.a[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main(){
AMGraph G;
Creat_UDN(G);
return 0;
}


